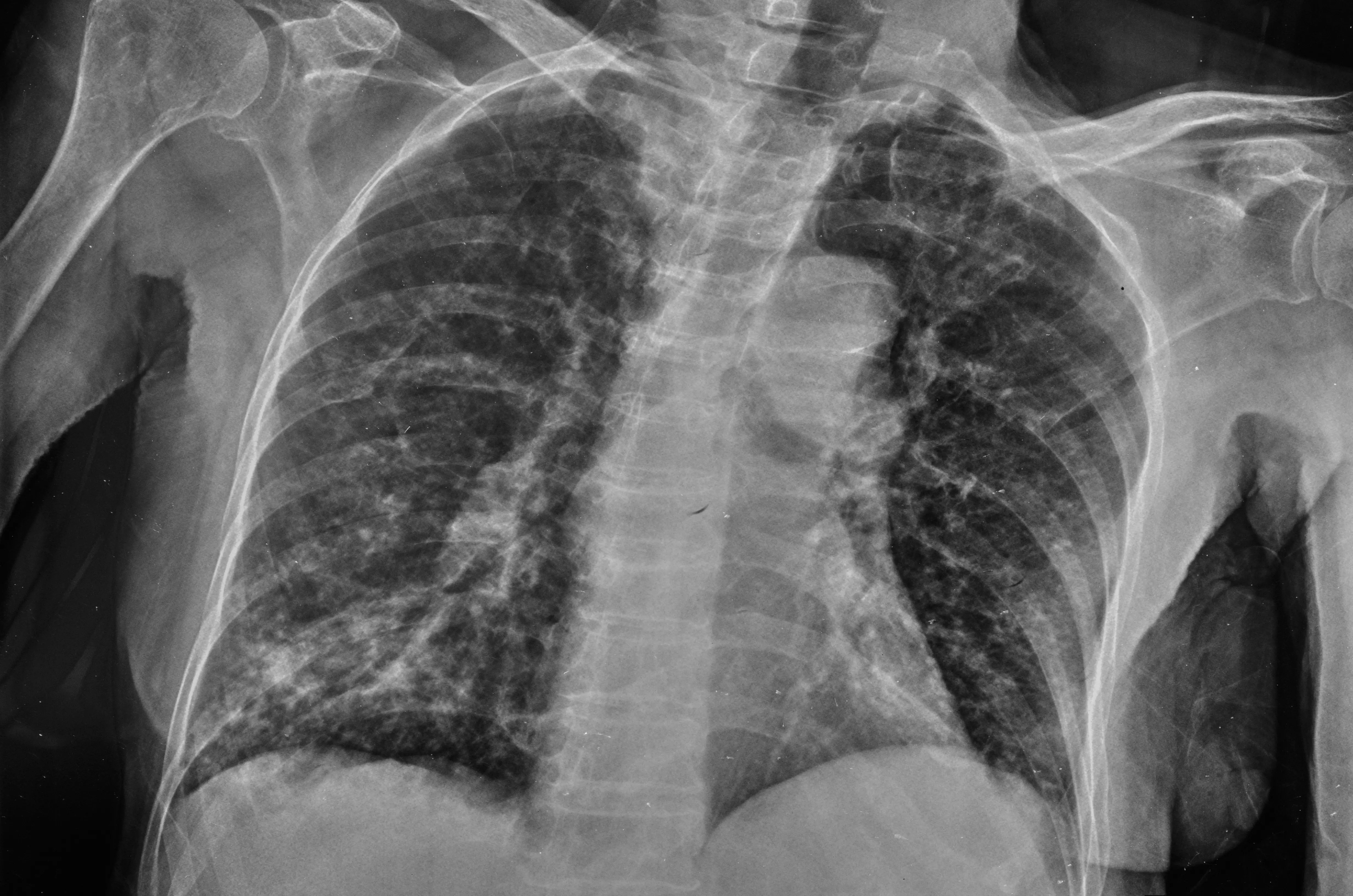
Pulmonary mycosis: Symptoms, causes, treatment
Lungworm is an infection of the respiratory tract caused by various types of fungi. While some of them are common and usually harmless to people with strong immune systems, they can be serious for people with weakened immune systems. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms, causes and treatment of lungworm.
What is lungworm?
Lungworm is a type of lung infection that is caused by fungi. This fungus can be local and limited to the lungs, or it can spread to other parts of the body. The most common pulmonary mycosis includes aspergillosis, histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis and blastomycosis.
Symptoms of pulmonary mycosis fungoides
Symptoms of pulmonary mycosis fungoides are often similar to those of other respiratory conditions, such as influenza or pneumonia. They may include:
A cough that may be dry or may be accompanied by sputum
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Fever
Loss of appetite and weight loss
Weakness and fatigue
Causes of lungworm
A fungal infection of the lungs usually results from inhaling fungal microorganisms present in the air. Some fungi that can cause lung infections are common in certain environments. For example, Histoplasma is often found in soil containing bird or bat droppings, while Aspergillus is common in indoor and outdoor air.
Although anyone can contract lungworm, some people are at higher risk, including:
People with weakened immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS patients or organ transplant recipients
People with chronic lung diseases, such as COPD or asthma
People who regularly take corticosteroids or other drugs that weaken the immune system